Computers are all around us, and they are one of the most widely used electronic machines on Earth. But I bet 90% of the users are not acquainted with its full form.
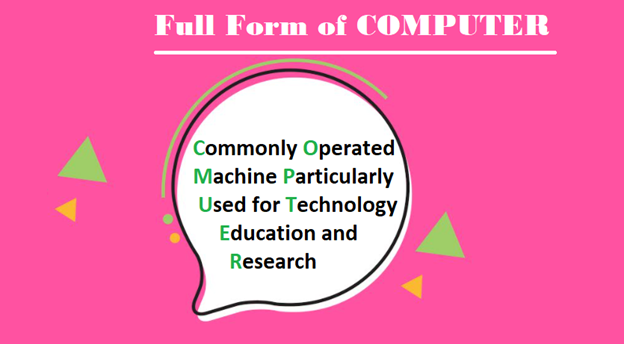
The full form of computer is ‘Commonly Operated Machine Particularly Used for Technology Education and Research’.
The break OF ‘C O M P U T E R’ is as follows:
C refers to ‘Commonly’
O refers to ‘Operated’
M refers to ‘Machine’
P refers to ‘Particularly’
U refers to ‘Used for’
T refers to ‘Technology’
E refers to ‘Education’ and
R refers to ‘Research’
Topics Covered
- What is Computer?
- Parts of Computer: Hardware/Software
- Generations of Computer
- Categorization on the basis of technology
- Full Form of Other Computer related Parts
What is Computer?
“Computers are an electronic device that manipulates the data by taking raw information as input and processing it to generate the output. It’s a gadget used to automate arithmetic and logical calculations and stores data in its memory.”
Computers are constantly bringing changes to our lives. From laptops to smartphones, smart watches have changed our vision to see and unite with the world.
The computer visualizes the specified data as ones or zeros and further compiles them in much more complex things such as images, videos, audio, website, etc.
Parts of Computer: Hardware/Software
The designing and implementation of a computer uses a combination of hardware and software.
- Hardware
The term ‘Hardware’ refers to the physical components of the computer including the internal and external parts.
The various internal hardware parts are as follows:
- CPU (Central Processing Unit)
- RAM (Random Access Memory)
- Motherboard
- Fan
- Memory- hard drive, CD –Rom, Floppy Drive
- Video card
- Cables
- Audio Card
- Battery
The various external hardware parts are as follows:
- Mouse
- Keyboard
- Monitor
- Joystick
- Projector
- Scanner
- Speaker
- Software
Software refers to the set of instructions that direct the computer or the hardware devices to get the desired output. Examples of software are a web browser, video player, or word processor.
Generations of Computer
The Generations of Computer is detailed information about how the hardware and software have evolved. They are distinguished based on technological changes.
First Generation Computers : Vacuum Tubes (1945 to 1956)
- The first generation computers used the integration of thousands of vacuum tubes.
- They were very large and, as a result, consumed a lot of power.
- First Generation computers were very expensive
- Punch cards and Paper Tapes were used to program it.
- They were very expensive and were used only in big offices.
- Examples: UNIVAC
Second Generation computer: Transistors (1956 to 1963)
- In 1956, transistors replaced the vacuum tubes and started the era for second-generation computers.
- Transistors made the computers compact, faster, less expensive than first generation and more reliable.
- They were more efficient but they still pursue the drawback of huge electricity consumption.
- Second Generation computers used Magnetic core technology to store instructions.
- Examples: IBM 7090
Third Generation Computers: Integrated Circuits (1964 to 1971)
- Third Generation computers used Integrated circuits (IC), making the computer smaller, cheaper and faster.
- They were accessed through keyboards, monitors and also the operating system.
- They became popular in the general public, and people started using them in their day-to-day lives.
- Examples: IBM 360 and PDP 11
Fourth Generation Computer: Microprocessors and IC (1972 till today)
- This generation was introduced with Microprocessors, which used VLSI (very-large-scale integration) technology to embed millions of Integrated Circuits (IC) on a single chip.
- Microprocessors transformed the computers into a more compact, handy, portable, cheaper and speedy machine with impeccable accuracy and reliability.
- They supported a larger memory and led to the explosion of GUI software and application software.
- Example: Laptops, Desktop, Tablets
Fifth Generation computers: ULSI (2010 – present)
- Fifth Generations computers are our future. They use ULSI (ultra large scale integration) technology.
- This generation computers will possess thinking capabilities i.e. Artificial Intelligence.
- Fifth generation computers work upon parallel processing hardware and AI software.
Categorization on the Basis of Technology and size
The computers can be classified based on the technology and size being used as:
- Analog Computer
An Analog Computer is capable of working on unpredictable aspects of physical phenomenon unlike electrical voltage, fluid pressure and mechanical quantities, etc. These computers are used to process the information generated by ongoing physical factors. Analog computers are not for day-to-day life works and are only used for special engineering and scientific applications. They are slower than digital computers.
Examples: Speedometer, Thermometer, Conventional Watch
2. Digital Computer
Digital computers are used to solve queries by processing data in discrete format. They are capable of processing numeric as well as non-numeric information. It is also used to perform arithmetic operations like sum, subtraction, multiplication, division and logical operations (AND, OR, NOT, NAND, etc.). The computers available today are digital computers.
Examples: Desktop, Laptop, Mobile Phones, iPad, and scientific calculators.
3. Hybrid Computer
As the name suggests, Hybrid computers are a combination of both analog and digital technology. It supports the prompt speed of analog and the impeccable accuracy of digital computers. They are capable of accepting digital or analog signals but it executes an extensive conversion of data from digital to analog. They are mostly found in hospitals to calculate the heartbeat of patients, at petrol pumps and in research industries.
Examples: ATM (Automated Teller Machine), Devices used at Petrol Pump
4. Supercomputer
Supercomputers are the fastest and largest of all computers. They are highly efficient for conducting typical mathematical calculations. Thus, they are very expensive and are only afforded by government agencies or big corporations to conduct specialized applications. They are used in weather forecasting, nuclear energy research and petroleum exploration.
5. Mainframe Computer
Mainframe Computers carry large size, high processing power, and vast amounts of memory and extraordinary level of reliability. They are only used for missionary applications which need high chunks of data processing. Universities, banking institutions, insurance companies use Mainframe commuters to maintain their volumes of data and records.
6. Mini Computer
Mini Computers are capable of supporting two or more users working on the same computer. They are of intermediate size and are mostly used for the business organization where the computers are interconnected.
7. Micro or Personal Computer
Microcomputer comprises a CPU (Central Processing Unit) as microprocessors. They are widely popular and mostly used for day-to-day personal and professional use.
Full Form of Other Computer related Parts
| SNO | Computer Part | Full Form | Specification |
| 1 | CPU | Central Processing Unit | CPU is one of the important components which provide the processing power to the computer.It is responsible for performing all the arithmetic and logical calculations.It is also known as the brain of the computer. |
| 2 | ALU | Arithmetic Logical Unit | The arithmetic logical Unit or ALU is the combinational digital electronic circuit that performs arithmetic and bitwise integer binary numbers.It is further divided into AU (arithmetic unit) and LU (logical unit). |
| 3 | LAPTOP | Lightweight Analytical Platform with Total Optimized Power | The laptop is a portable personal computer with all the features and functionality of a desktop computer. |
| 4 | RAM | Random Access Memory | RAM holds all of the computer data that you are currently working upon.It is also referred to as short term memory. |

